Beginner's guide to Search Engine Optimsation (SEO)

Ecommerce
148 week ago — 11 min read
With 400 million active websites in the world, driving traffic to your website requires skill and effort. One of the most obvious ways to drive more traffic to your website is by investing in Search Engine Optimisation (SEO).
What is SEO?
SEO is the process of improving the visibility of a website on a search engine’s results page. The higher and more frequently a site appears in the search results, the more visitors it will receive from the search engine.
The ease with which your target clients may reach you is determined by your SEO approach. That's no simple feat, given that 75% of internet users don't even browse past the first page of search results.
Understanding types of web traffic
You can get various kinds of traffic from search engines and SEO can assist in attracting each of these.
Quality traffic: Suppose you own a fashion website. People who are looking for insurance, on the other hand, are being directed to your website because the search engine included your website in its search results. Users interested in insurance, in this case, do not bring any value to your website and are more likely to leave. SEO helps you attract high-quality visitors who are more likely to convert.
Quantity traffic: The more individuals that see your website through a SERP (Search Engine Results Page), the better! SEO aids in the visibility of your website in search engines.
Organic traffic: Have you ever observed that when you look for a product, an advertisement appears almost everywhere? Yes, it's possible to find it on social media and even in search engines. Paid traffic is defined as website traffic generated by advertisements (the user clicking on the advertisement). Organic traffic, on the other hand, is when your website gets discovered by visitors on the SERP without having to pay for it.
SEO, when broken down further, can be described as a two-way street. Your potential visitors are looking for "what your website has to offer," and you are the website that has it. SEO serves as a link between the two, assisting in the successful narrowing down of both parties' demands and desires.
How do search engines work?
Now that we've understood what SEO is, let’s look at how search engines work. Search engines are automated response systems. They exist to find, understand, and organise content on the internet in order to provide the most appropriate answers to searchers' requests.
Your website must first be visible to search engines in order to appear in search results. It's perhaps the most crucial aspect of SEO: if your website can't be found, there's no chance you'll ever appear in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page).
Let’s grasp three fundamental terms that are critical to the operation of a search engine and, by extension, SEO:
Crawling - The first step is the discovery process. Crawling is the process of discovering what content is available on the internet. Crawlers or spiders (this is the term for bots) are sent by search engines to find new information and add it to their database of recognised pages. Links can be used to locate this information. The content can be a website, an image, text, a document, a video, or anything else.
Indexing - The next stage is to decipher the data gathered by the crawlers. This is referred to as indexing. The search engine (for example, Google) tries to interpret and analyse the content of the pages it finds before storing them appropriately. In a nutshell, the data is saved in an index, which is a huge database, hence the name. The way your page is indexed (stored) in Google has a direct correlation with how many people find it. Here are some Google tips to help you effectively index your page:
-
Page titles should be brief but informative.
-
Use appropriate page headings.
-
Text material is preferred above media (pictures, audio, and video).
Ranking - Ranking is the final element of the puzzle. When a user types a query into a search engine, the search engine displays the results based on what it considers to be the most relevant. The index is used to obtain this information. The results are ordered in order of 'most relevant' to 'least relevant,' as you can see. To increase your search engine rankings and make it easier for users to find your homepage, make sure your material is correctly indexed, up-to-date, and that your website is fast, secure, mobile-friendly, and optimised. Use keywords (the most relevant phrases that users search for in relation to your webpage content) in your content to optimise it.
SEO Basics & Guidelines
1. Make sure your website is crawled by Google
Google Search Console offers free tools and services to make your more website relevant and correct any content or tech related issues.
2. Understanding web search results
3. Keyword Research
Keyword research is a technique used by search engine optimisation professionals to identify and research search terms that people use while looking for products, services, or general information in search engines.
Google offers free keyword planner tool to find keywords for your website. It shows complete search report (volume, competition, monthly break up, location search etc).
Keywords can be short tail or long tail. Short tail keywords are generic words like ‘red shoe’ whereas long tell keywords are actual terms users are searching Eg. ‘Nike red shoe for football in Delhi’. It is advisable to start with long tail keyword and gradually shift to short tail in long-term.
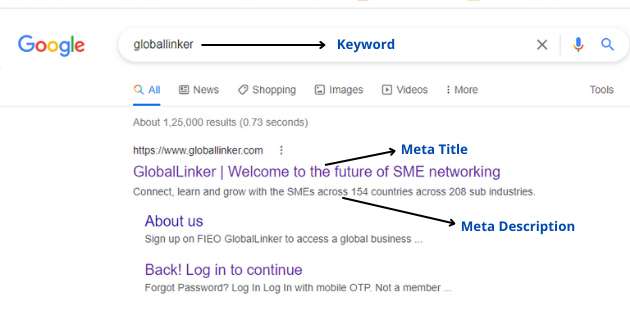
4. Meta Title
As per Google, titles are critical to giving users a quick insight into the content of a result and why it’s relevant to their query. It's often the primary piece of information used to decide which result to click on, so it's important to use high-quality titles on your web pages.
Here are some best practices for Meta Titles.
-
Length – Maximum of 65 characters
-
Add distinct, descriptive titles for each page on site
-
Avoid generic and vague titles
-
Use sentence case or title case
-
Include your target keyword where it makes sense
5. Meta Description
A Meta Description informs and interests users with a short, relevant summary of what a particular page is about. Google doesn’t always show the meta description you set. Sometimes they show a different snippet.
Here are some best practices for Meta Description.
-
Length – Maximum of 160 characters
-
Add distinct, descriptive description for each page on site
-
Avoid generic and vague description
-
Use sentence case
-
Include your target keyword where it makes sense
6. URL Structure
The URL sends a signal to search engines about its topic.
-
Avoid changing it over time.
-
Use readable words rather than long ID numbers
Avoid: http://www.example.com/index.php?id_sezione=360&sid=3a5ebc944f41daa6f849f730f1
Recommended: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aviation
-
Use target keyword but don’t spam
7. Optimise your product descriptions
A product page is especially crucial for an ecommerce website. A product page contains numerous aspects that all require attention. To gain visitors' attention and get them to click through, you'll also want a few things to stand out on the page.
To begin optimising your ecommerce product pages, keep the following three points in mind:
-
What are the most important aspects of the page?
-
How can you make the most of these elements in terms of visibility and impact?
-
What can you do with this information to increase the effectiveness of your product description?
Start thinking about how you can improve the effect of your product descriptions now. This could include items like as.
-
Including many, high-quality, one-of-a-kind pictures
-
Including keywords
-
Providing keyword-rich, thorough descriptions
-
Incorporating clear call to actions
-
Provide captions (with alt tags) for pictures.
-
Use the right keywords in file names.
8. Linking strategy
Internal Linking
-
Create a strong structure with plenty of links between relevant pages
-
Find relevant page for linking through Google Search: site:yourdomain.com + “topic of the post you want to link to”
-
Use appropriate anchor text - Avoid generic anchor text like "page", "article", or "click here".
-
Aim for short but descriptive text-usually a few words or a short phrase
-
Use keyword as anchor text but don’t spam
External Linking
-
Link only to those websites which adds value to page content
-
Every link takes away page reputation and adds to linking website
9. Website content
Your concentration should be on two fronts when it comes to website content. To begin, strive to include as many of your important keywords as possible at the start of your article. Second, use as many keywords or keyword phrases as feasible throughout the text. Although repetition is beneficial, overt repetition will result in a penalty.
Digital Marketer and SEO expert, Todd Malicoat has said, “SEO is a noun, verb and adjective.”
Indeed, SEO has so many facets to it, and the work never ends. We have discussed here the tip of the iceberg. To learn more about SEO, check out this guide by Google.
GlobalLinker conducted a webinar with a leading SEO expert on tips to drive more traffic to your website through Search Engine Optimisation. Watch the highlights of the webinar below.
Image source: Canva
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views, official policy or position of GlobalLinker
Posted by
GlobalLinker StaffWe are a team of experienced industry professionals committed to sharing our knowledge and skills with small & medium enterprises.
Network with SMEs mentioned in this article
View GlobalLinker 's profile
SME Inspirations
Most read this week
Trending
What is BRC in Export Business?
Export Sector 1 week ago














Comments (1)
Share this content
Please login or Register to join the discussion